How to write a program to print Pascal Triangle in C language with an example? The Pascal is a triangle with an array of binomial coefficients.
C Program to print Pascal Triangle
This Pascal triangle in the C program allows users to enter the maximum number of rows to print. We will print the Pascal triangle of integers until it reaches the user-specified rows.
#include <stdio.h>
long Factorial(int);
int main()
{
int i, Number, j;
printf("\n Please Enter the Number of rows you wish to see \n");
scanf("%d", &Number);
for (i = 0; i < Number; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= (Number - i - 2); j++)
{
printf(" ");
}
for (j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
printf("%ld ", Factorial(i) / (Factorial(j) * Factorial(i-j)));
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
long Factorial(int Number)
{
int i;
long Fact = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= Number; i++)
Fact = Fact * i;
return Fact;
}
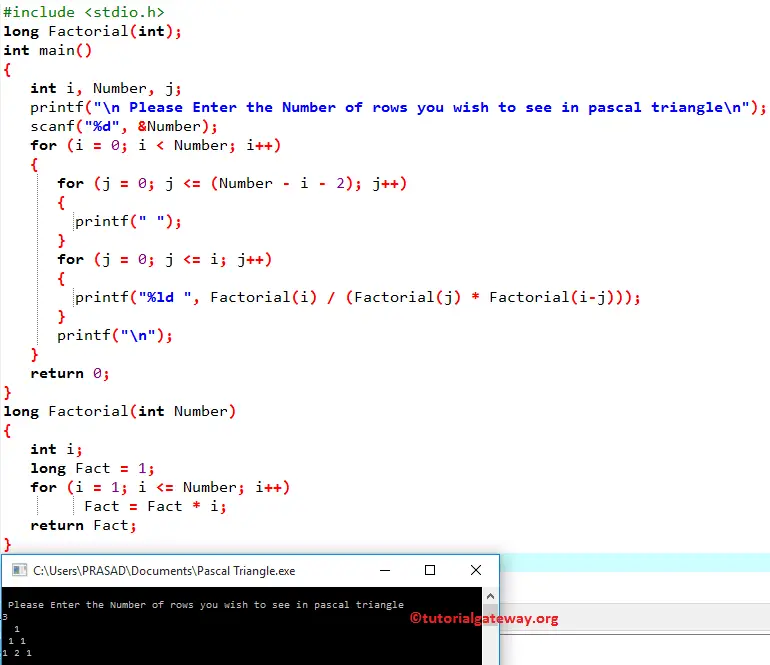
Within this pascal triangle in C example, the long Factorial(int Number) function declaration will find the factorial of the given number. Please refer C Program to Find Factorial of a Number to understand the steps involved in the first function.
The following C Programming printf and scanf statements will allow entering the range or maximum Number of rows to print as a Pascal triangle.
Analysis
Now let us see the Nested for loop iteration wise.
Outer Loop – First Iteration
From the above C Pascal triangle screenshot, you can observe that the value of i is 0, the Number is 3, and the condition (i < 3) is True. So, it will enter into the second for loop.
First Inner Loop – First Iteration
The j value is 0, and the condition (j <= (3 – 0 – 2) is True. So, it will start executing the statements inside the loop. The printf(” “) statement will print Empty space as Output
The following j++ statement will increment the Value of j by 1 using the Increment Operator.
Pascal Triangle in C program First Inner Loop – Second Iteration
The j value will be 1, and the condition (1 <= (3 – 0 – 2)) is True so that the following statement will print Empty space as Output
First Inner Loop – Third Iteration
The j value will be two, and the condition (2 <= (3 – 0 – 2)) is False. So, it will exit from the for loop.
Next, it will enter into the second For Loop
for (j = 0; j <= i; j++) // Second Inner Loop
{
printf("%ld ", Factorial(i) / (Factorial(j) * Factorial(i-j)));
}
Second Inner Loop – First Iteration of C Program to print Pascal Triangle
We haven’t finished the first iteration of the Outer for loop, so i value is still 0.
The j value is 0, and the condition (j <= 0) is True. So, it will start executing the statements inside the loop. The following statement will find the factorials of i and j and prints the output
printf("%ld ", Factorial(i) / (Factorial(j) * Factorial(i-j)));
factorial(i) / (Factorial(j) * Factorial(i – j) )
It means, factorial(0) / (Factorial(0) * Factorial(0) ) —> Factorial of 0 = 1
= 1 / (1 * 1) = 1
The j++ statement will increment the value of j by 1 using the Increment Operator.
Second Inner Loop – Second Iteration
The j value will be 1, and the condition (1 <= 0) is False. So, it will exit from the for loop. The following printf(“\n”) statement is to terminate the current line.
Final Output after the First Iteration = [Empty Space] [Empty Space] 1
Pascal triangle in C program Outer Loop – Second Iteration
The value of i will be 1, and the condition (1 < 3) is True. So, it will enter into the second for loop.
First Inner Loop – First Iteration
The value of j is 0 and the condition (0 <= 0) is True. So, empty space will print as output. Next, the j value will also be incremented by 1.
First Inner Loop – Second Iteration
The value of j is 1, and the condition (1 <= 0) is False. So, it will exit from the for loop. Now, it will enter into the second For Loop.
Second Inner Loop – C Program to print Pascal Triangle First Iteration
We haven’t finished the second iteration of the Outer for loop, so i value is still 1.
The j value is 0, and the condition (0 <= 1) is True. So, it will start finding the factorials of i and j and prints the output
factorial(i) / (Factorial(j) * Factorial(i – j) )
It means, factorial(1) / (Factorial(0) * Factorial(1) ) —> Factorial of 0 = 1
= 1 / (1 * 1) = 1
Second Inner Loop – Second Iteration of C Pascal triangle
The j value will be 1, and the condition (1 <= 1) is True. So, it will start finding the factorials of i and j and print the output
factorial(1) / (Factorial(1) * Factorial(0) ) —> Factorial of 0 = 1
= 1 / (1 * 1) = 1
Second Inner Loop – Third Iteration
The j value will be 2, and the condition (2 <= 1) is False so that it will exit from the for loop. Final Output after the Second Iteration = [Empty Space] 1 1
Pascal triangle in C Outer Loop – Third Iteration
The value of i will be 2, and the condition (2 < 3) is True. So it will enter into the second For Loop.
Second Inner Loop – First Iteration
We haven’t finished the third iteration of the Outer for loop, so i value is still 2.
The j value is 0, and the condition (0 <= 2) is True. So, it will start finding the factorials of i and j and print the output
factorial(2) / (Factorial(0) * Factorial(2) ) —> Factorial of 0 = 1
= 2 / (1 * 2) = 1
Second Inner Loop – Second Iteration
The j value will be 1, and the condition (1 <= 2) is True.
factorial(2) / (Factorial(1) * Factorial(1) ) —> Factorial of 2 = 2
= 2 / (1 * 1) = 2
Second Inner Loop of the program – Third Iteration of C Pascal triangle.
j = 2, and the condition (2 <= 2) is True.
factorial(2) / (Factorial(2) * Factorial(0) )
= 2 / (2 * 1) = 1
Second Inner Loop – Fourth Iteration
j = 3, and the condition (3 <= 2) is False. So, it will exit from the for loop. The final output after the Third Iteration = 1 2 1
Outer Loop – Fourth Iteration
The value of i will be 3, and the condition (3 < 3) is False. So it will exit from the for loop.
Final Output is:
[Empty Space] [Empty Space] 1
= [Empty Space] 1 1
1 2 1
C Program to print Pascal Triangle using recursion
This C program allows the user to enter the number of rows to print as a Pascal triangle. We will use the code snippet we used in our first example in this example. However, this time we are using the recursive function to find factorial.
#include <stdio.h>
long Factorial(int Number)
{
if (Number == 0 || Number == 1)
return 1;
else
return Number * Factorial (Number -1);
}
int main()
{
int i, Number, j, Fact;
printf("\n Please Enter Number of rows you want to see \n");
scanf("%d", &Number);
for (i = 0; i < Number; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j <= (Number - i - 2); j++)
{
printf(" ");
}
for (j = 0; j <= i; j++)
{
Fact = Factorial(i) / (Factorial(j) * Factorial(i-j));
printf("%ld ", Fact);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
Please Enter Number of rows you want to see
9
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
1 6 15 20 15 6 1
1 7 21 35 35 21 7 1
1 8 28 56 70 56 28 8 1 
Comments are closed.