The SQL Server While Loop is used to repeat a block of statements for a given number of times until the given condition is False. The SQL While loop starts with the condition, and if the condition result is True, then statements inside the BEGIN..END block will execute. Otherwise, it won’t execute. It suggests that the while loop may execute zero or more times.
SQL While loop Syntax
The Syntax of a While Loop in SQL Server is as follows:
While Expression
BEGIN
statement 1
statement 2
………….
END
-- This is the statement Outside the block
First, the condition inside the SQL Server While loop was tested. If the condition is True, the statement or query inside the BEGIN..END block will execute. If the condition is False, it will skip the BEGIN..END block and execute other statements outside of it.
SQL Server While Loop Flow Chart
The following flow chart will explain to you While loop Visually and perfectly.
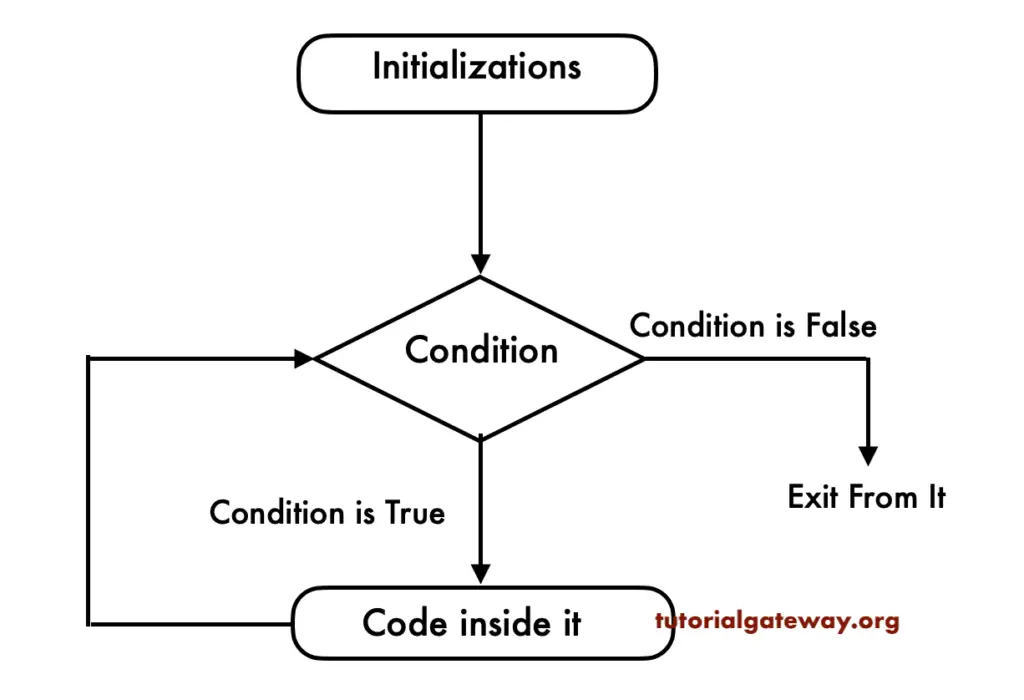
The SQL Server While loop will check the condition at the beginning of it.
- If the condition is True, it executes the code within the BEGIN..END statements.
- Within the While loop, we must use the Arithmetic Operators to increment and decrements the value.
- After the value increase, again, the Server checks the condition. As long as the condition is True, it continues the process.
- If the expression is evaluated to False exits from the BEGIN..END block.
Let us see the example for a better understanding
SQL Server While Loop Example
In this example, we declared two integer values. Next, we used the While loop to add numbers from 1 to 10.
--Declaring Number and Total Variables DECLARE @Number INT = 1 ; DECLARE @Total INT = 0 ; WHILE @Number < = 10 BEGIN SET @Total = @Total + @Number; SET @Number = @Number + 1 ; END PRINT @Total;
Total = 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 + 9 + 10 = 55
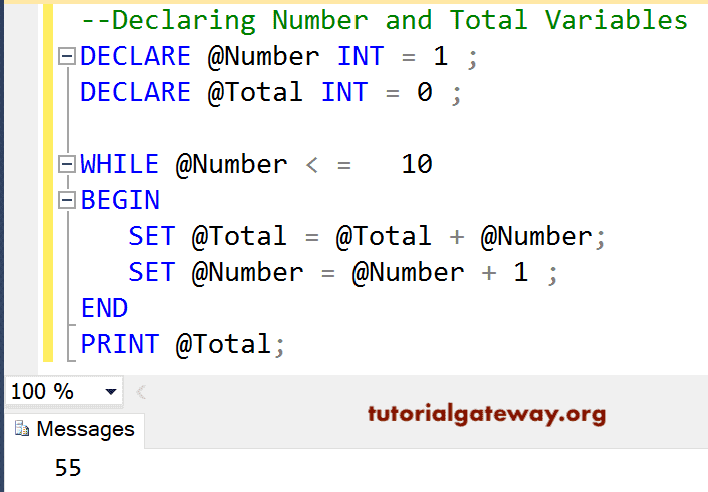
In this query, we first created two variables called Number and Total and initialized them to 1, and 0 using the following statement.
DECLARE @Number INT = 1 ; DECLARE @Total INT = 0 ;
In the next line, we used the SQL Server while loop condition. If the condition result is true, the number is added to the total. Otherwise, it will exit from the iteration. We also SET the Number value to increment (@Number = @Number + 1). After increment, the process will be repeated until the condition results False (i.e., @Number = 11).
WHILE @Number < = 10 BEGIN SET @Total = @Total + @Number; SET @Number = @Number + 1 ; END
Here, we used a print statement outside the while loop. This statement will execute when the condition is either True or False.
PRINT @Total;
SQL Server Infinite While Loop
If you forget to increment (SET @Num = @Num + 1) or decrement the value, the SQL while loop will execute countless times, also called an infinite loop. For example:
-- Infinite Example --Declaring Num and Total Variables DECLARE @Num INT = 1 ; WHILE @Num < = 10 BEGIN PRINT @Num; -- SET @Num = @Num + 1 ; END
Output
Messages
-------
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
.
.
.Here Number is constantly 1, and it is always less than ten. So PRINT statement inside the while loop will go on executing countless times. Now, let us remove the comment from the following statement.
-- SET @Num = @Num + 1 ;
Now, when it reaches 10, the condition will fail. Let us see the output.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10SQL Nested While Loop
The Nested SQL While Loop is nothing but placing While Loop inside another While Loop. SQL Server Nested While loops are instrumental when working with multi-layered data. Because when we want to select the layered data, we have to use this SQL Nested While loop to extract the layered data. But please be careful while using it.
Nested SQL While Loop Syntax
The syntax of the Nested While Loop in SQL Server is
WHILE Expression BEGIN WHILE @Val2 <= 10 BEGIN -- Second While Loop Statements Statement 1 Statement 2 ........... Statement N END -- Below Statements are Outside the Second While Loop -- First While Loop Statements Statement 1 Statement 2 ........... Statement N END -- This Statement is Outside the First While Loop
If you observe the above Nested SQL While Loop syntax, We placed the While loop inside another While loop. We already explained the While loop syntax in our previous article.
Step 1: First, it checks for the condition inside the first While loop.
- If the expression result is True, the begin and end code block inside the While loop will execute. Next, it will start the second While loop. Go to Step 2
- If the result is False, it will exit from While Loop
Step 2: It will verify the condition in the Nested SQL While Loop (second While loop).
- If the result is True, the code inside the second While loop begin…end will execute. It means SQL Server runs statements from Statement 1 to N.
- If it is False, it exits from the second While Loop.
3rd Step: Once it exit from the second While loop, it will check for the condition inside the first While loop (repeating Step 1 )
Nested SQL While Loop Example
This SQL Nested While loop program will print the Multiplication table of 1 and 2 up to 10. For this, we will nest one While loop inside another, called nested SQL While Loop.
--Nested SQL While Loop Example DECLARE @Val1 INT, @Val2 INT SET @Val1 = 1 WHILE @Val1 <= 2 BEGIN SET @Val2 = 1 WHILE @Val2 <= 10 BEGIN PRINT CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val1) + ' * ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val2) + ' = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val1 * @Val2) SET @Val2 = @Val2 + 1 END SET @Val1 = @Val1 + 1 END
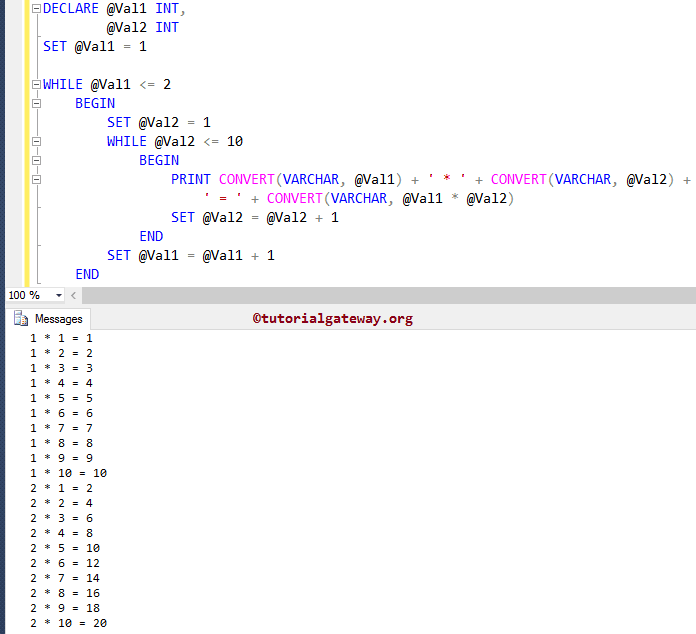
Within this SQL Nested While Loop example, we first created two variables called Val1 and Val2 and then initialized the @Val1 to 1 using the following statement.
DECLARE @Val1 INT, @Val2 INT SET @Val1 = 1
In the next line, we used the SQL Server while loop with expression. If the expression result is true, it will enter to Nested While loop.
WHILE @Val1 <= 2 BEGIN SET @Val2 = 1 WHILE @Val2 <= 10 BEGIN PRINT CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val1) + ' * ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val2) + ' = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val1 * @Val2) SET @Val2 = @Val2 + 1 END SET @Val1 = @Val1 + 1 END
From the above screenshot, you can observe that this Nested SQL While Loop query prints multiplication table for 1 and 2.
First While Loop First Iteration
In the first While loop, @Val1 is initialized to 1, and then it will check whether @Val1 is less than or equal to 2. This condition (1 <= 2) is True, so it will enter into a second While loop
Nested SQL While Loop or Second While Loop First Iteration
In the second While loop, @Val2 is initialized to 1, and check whether @Val2 is less than or equal to 10. This condition is True. So, the statements inside the second While loop will execute
PRINT CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val1) + ' * ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val2) +
' = ' + CONVERT(VARCHAR, @Val1 * @Val2)
@Val1 * @Val2 ==> 1 * 1 = 1
Next, the @Val2 value will be incremented by 1 (SET @Val2 = @Val2 + 1). Please refer Arithmetic Operators article to understand the + notation.
Second While Loop Second Iteration
Here, @Val2 is incremented by one. So, @Val2 =2. It will check whether @Val2 is less than or equal to 10. This condition (2 <= 10) is True. So, it will execute the statements inside the second While loop
@Val1 * @Val2 ==> 1 * 2 = 2
Next, the @Val2 value will increment by 1.
This process will repeat until @Val2 reaches 11. Once the condition inside the SQL nested While loop fails, the compiler will exit from the second While loop, and the @Val1 value will increment by 1 (SET @Val1 = @Val1 + 1).
First While Loop Second Iteration
@Val1 = 2. Check whether @Val1 is less than or equal to 2. This condition ( 2 <= 2) is True, so it enters into a second While loop
Second While Loop First Iteration
Within the second While loop, @Val2 will initialize to value 1 and check whether @Val2 is less than or equal to 10. This condition is True, so it executes the statements inside the second While loop
@Val1 * @Val2 ==> 2 * 1 = 2
Next, the @Val2 value will increment by 1 (SET @Val2 = @Val2 + 1).
Second While Loop Second Iteration
Here, @Val2 will increment by 1, so @Val2 = 2. Next, it will check whether @Val2 is less than or equal to 10. The condition (2 <= 10) is True, so it will start executing the statements inside the second While loop
@Val1 * @Val2 ==> 2 * 2 = 4
Next, the @Val2 value will increment by 1 (SET @Val2 = @Val2 + 1)
This process will repeat until @Val2 reaches 11. Once it reaches 11, the condition (11 <= 10) inside the second While loop fails. So, it will exit from the nested While loop, and the @Val1 value will increment by 1 (SET @Val1 = @Val1 + 1).
First While Loop Third Iteration:
Here, i = 3 means the expression (@Val1 <= 2) will be False. So, While loop will terminate, remember, no need to check the second loop.
