The Java charAt method is one of the String Methods, which is to return the character at the specified index position. This article will show how to write string charAt in Java Programming language with an example.
Java charAt Syntax
The basic syntax of the string charAt in Java Programming language is as shown below.
public char chatAt(int Index_Position) //In order to use in program String_Object.charAt(int Index_Position)
- String_Object: Please specify the valid String Object to find the character.
- Index_Position: Please specify the index position of the desired character.
The Java charAt Function will return the Character from String_Object at the specified Index_Position. If we specify the Index position out of range, the chartAt Function will throw an error.
TIP: The position of an index will start from 0, Not 1.
Java charAt Example
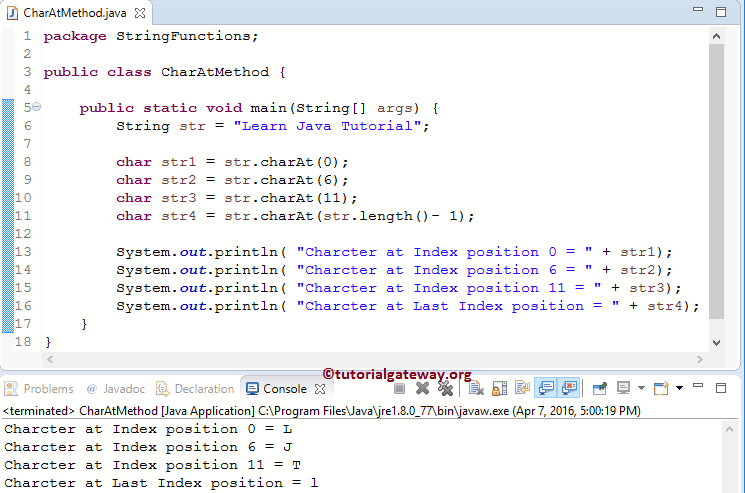
In this Java program, we will use the string charAt method to return the Character at the given index position.
Within this example, we declared the String variable and assigned a value using the first statement.
The following three statements will use the Java charAt, find Characters at index positions 0, 6, and 11, and store the characters in str1, str2, and str3 variables of type char.
NOTE: For the charAt String Method, you should count the space as One Character.
In the next line, we use the length function to find the string length. In this code snippet, we subtract one from the string length. Because the length of a string will count from 1 to n, where the index position will start from 0 to n – 1.
The following System.out.println statements will print the output
package StringFunctions;
public class CharAtMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Learn Java Tutorial";
char str1 = str.charAt(0);
char str2 = str.charAt(6);
char str3 = str.charAt(11);
char str4 = str.charAt(str.length()- 1);
System.out.println( "Charcter at Index position 0 = " + str1);
System.out.println( "Charcter at Index position 6 = " + str2);
System.out.println( "Charcter at Index position 11 = " + str3);
System.out.println( "Charcter at Last Index position = " + str4);
}
}
charAt Example 2
In this string charAt program, we will ask the user to enter Y or N. The Java charAt program will display the message based on the user-entered character.
package StringFunctions;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class CharAtMethod2 {
private static Scanner sc;
public static void main(String[] args) {
sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("\nPlease Enter Y or N letter: ");
String letter = sc.next();
char ch = letter.charAt(0);
if (ch == 'y' || ch == 'Y') {
System.out.println("Hey!! Welcome to Library");
}
else {
System.out.println("Goodbye to Library");
}
}
}
Please Enter Y or N letter:
y
Hey!! Welcome to LibraryLet us enter the different characters as the charAt argument
Please Enter Y or N letter:
N
Goodbye to LibraryThe first two statements will ask the user to enter Y or N character. Next, we assign the user-entered value to the letter variable.
For the ch variable, we are checking the character at the Zero index position using the Java string charAt method.
Next, we used the If Else Statement to check whether the character at index position zero is y / Y or not.
- If it y or Y System.out.println(“Hey!! Welcome to Library”); statement will be printed
- Else System.out.println(“Goodbye to Library”); statement will be printed.
We can use the lowercase method to convert user input to lower also but to make the code easy, we are going in the standard way.
