This C# section covers the list of available Date and time formatting options in C# programming language and a practical example.
C# DateTime to format date and time
The C# DateTime is a struct available from System Namespace in the DotNet framework to format date and time. Since DateTime is a struct, not a class, we know that structs are value types, i.e., DateTime can create as an object but not a reference. Since it is a value type, the variables or fields of DateTime cannot hold null values.
To store null values, they should convert to nullable types by using a question mark(?)
Ex: DateTime? dt = null
DateTime represents dates and times with a range of values from 00:00:00, January 1, 0001 through 11:59:59 P.M., December 31, 9999
Initializing the C# DateTime object
We can initialize the C# DateTime object in the following ways to format date and time.
Call a constructor, either the default constructor or the one which will take arguments.
For example, a default constructor of DateTime looks like
DateTime dt = new DateTime();
Outputs 1/1/0001 12:00:00 AM
A DateTime constructor overloaded with year, month, day, hour, minute, and second looks like this:
DateTime dt = new DateTime(2018, 6, 12, 8, 20, 58);
By assigning a value
Assigning a date and time value returned by a property or method to the DateTime object looks like.
DateTime dt = DateTime.Now;
DateTime dt = DateTime.AddDays(20);
Parsing a string to a C# DateTime value
Parse and TryParse are used in general to parse a string to its equivalent date and Time value.
DateTime dt = DateTime.Parse(“1985, 01, 14”);
Formatting Date and Time in C#
In general, the C# Date and Time format string use a format specifier to define the text representation of its value.
To define a text representation of the date and time value, if a single format specifier is used, then it is said to be a standard date and time format string.
If a date and time format string has more than one character, including the white space, it calls as a custom format string.
The following table shows the different C# date and time format specifiers and their results.
| Format Specifiers | Result |
|---|---|
| D | 30 July 2018 |
| D | 30-07-2018 |
| F | 30 July 2018 23:38:50 |
| F | 30 July 2018 11:38 PM |
| G | 30-07-2018 23:38:50 |
| G | 30-07-2018 11:38 PM |
| M | 30 July |
| r | Mon, 30 July 2018 23:38:50 GMT |
| s | 2018-07-30T23:38:50 |
| T | 23:38:50 |
| t | 11:38 PM |
| u | 2018-07-30 23:38:50Z |
| y | July, 2018 |
| dd | 30 |
| ddd | Mon |
| dddd | Monday |
| hh | 11 |
| HH | 11 |
| mm | 38 |
| MM | 07 |
| MMM | Jul |
| MMMM | July |
| ss | 50 |
| fff | 166 |
| FFF | 469 |
| tt | PM |
| yy | 18 |
| yyy | 018 |
| yyyy | 2018 |
The following table shows different custom C# Data and Time format strings and their results.
| C# Date and Time Formats | Result |
|---|---|
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“MM/dd/yyyy”) | 07/31/2018 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“dddd, dd MMMM yyyy”) | Tuesday, 31 July 2018 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“dddd, dd MMMM yyyy hh:mm”) | Tuesday, 31 July 2018 08:15 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“dddd, dd MMMM yyyy hh:mm tt”) | Tuesday, 31 July 2018 08:15 PM |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“dddd, dd MMMM yyyy h:mm”) | Tuesday, 31 July 2018 8:15 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“dddd, dd MMMM yyyy h:mm tt”) | Tuesday, 31 July 2018 8:15 PM |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“dddd, dd MMMM yyyy HH:mm:ss”) | Tuesday, 31 July 2018 20:15:06 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm”) | 07-31-2018 20:15 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“MM/dd/yyyy hh:mm tt”) | 07-31-2018 08:15 PM |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“MM/dd/yyyy H:mm”) | 07-31-2018 20:15 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“MM/dd/yyyy h:mm tt”) | 07-31-2018 8:15 PM |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“MM/dd/yyyy HH:mm:ss”) | 07-31-2018 20:15:30 PM |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“MMMM dd”) | July 31 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“yyyy-MM-dd T HH:mm:ss.fffffffK”) | 2018-07-31 T 00:34:54.0306280+05:30 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“ddd, dd MMM yyy HH: mm: ss GMT”) | Tue, 31 Jul 2018 34:54:03 GMT |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“yyyy-MM-dd T HH:mm:ss”) | 2018-07-31 T 20:15:30 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“HH:mm”) | 20:15 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“hh:mm tt”) | 08:15 PM |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“H:mm”) | 20:15 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“h:mm tt”) | 8:15 PM |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“HH:mm:ss”) | 20:15:06 |
| DateTime.Now.ToString(“yyyy MMMM”) | 2018 July |
C# Date and Time Formatting Example
Let us see a C# format date and time code and demonstrate different properties and methods of DateTime struct by using its object.
Just take a Windows form and add a button to it and write the following code in its button click event.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Data;
using System.Drawing;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Windows.Forms;
namespace WindowsFormsApp2
{
public partial class Form1 : Form
{
public Form1()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private void button1_Click(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
DateTime current_date1;
DateTime current_date2;
DateTime current_date3;
current_date1 = DateTime.Now;
MessageBox.Show(current_date1.ToString());
int day = current_date1.Day;
MessageBox.Show(day.ToString());
current_date2 = DateTime.Today;
MessageBox.Show(current_date2.ToString());
current_date3 = DateTime.Now.AddDays(30);
MessageBox.Show(current_date3.ToString());
string custom = current_date1.ToString("dddd, dd MMMM yyyy HH:mm:ss");
MessageBox.Show(custom.ToString());
}
}
}
OUTPUT
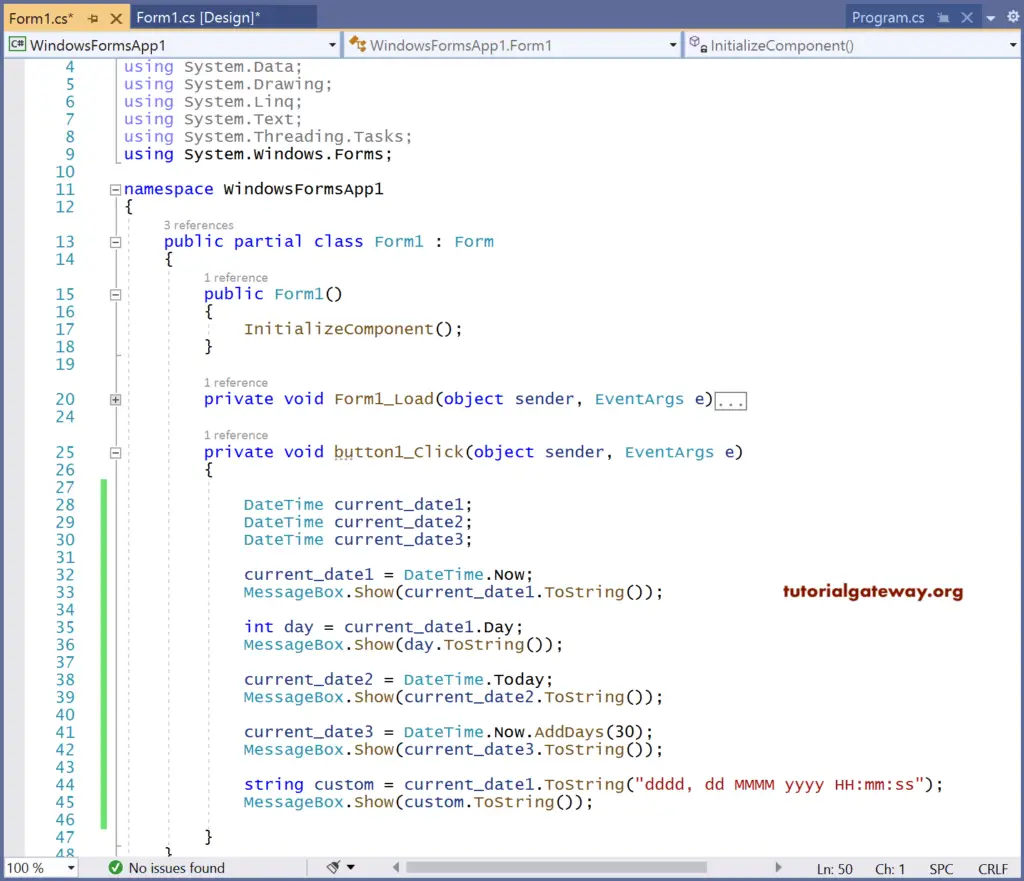
Once you run this C# date and time format project, the following window will open
When you click that button1, message boxes will display with the dates.
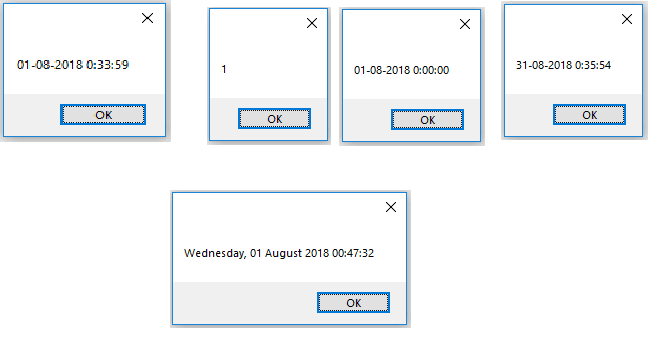
current_date1, current_date2, and current_date3 are the different objects created for DateTime.
Object current_date1 is used to display the current system date through the DateTime property.
DateTime.Now;
The current system date displays in the message box.
Same way as DateTime.AddDays(30) will display the date and time by adding 30 days to the current date.
Finally, we have tried to display the result of a custom format string ddd, dd MMMM yyyy HH:mm:ss.
