Write a Python program to convert Dictionary to Pandas DataFrame with an example. There are multiple ways to convert Dictionary to a pandas DataFrame, and we covered all of them.
In this example, first, we declared an employee dictionary and used the pandas DataFrame function. Within that, we are accessing the items. Second, we converted the dictionary items to a list and then converted the list to DataFrame.
import pandas as pd
empDict = {'name': 'Jhon Miller', 'Age': 32, 'Job': 'Developer'}
print(empDict)
df1 = pd.DataFrame(empDict.items())
print(df1)
df2 = pd.DataFrame(list(empDict.items()))
print(df2)
Converting Dictionary to pandas DataFrame output
{'name': 'Jhon Miller', 'Age': 32, 'Job': 'Developer'}
0 1
0 name Jhon Miller
1 Age 32
2 Job Developer
0 1
0 name Jhon Miller
1 Age 32
2 Job DeveloperThe pandas DataFrame has column attribute to assign names to columns, and we used that list to assign multiple column names.
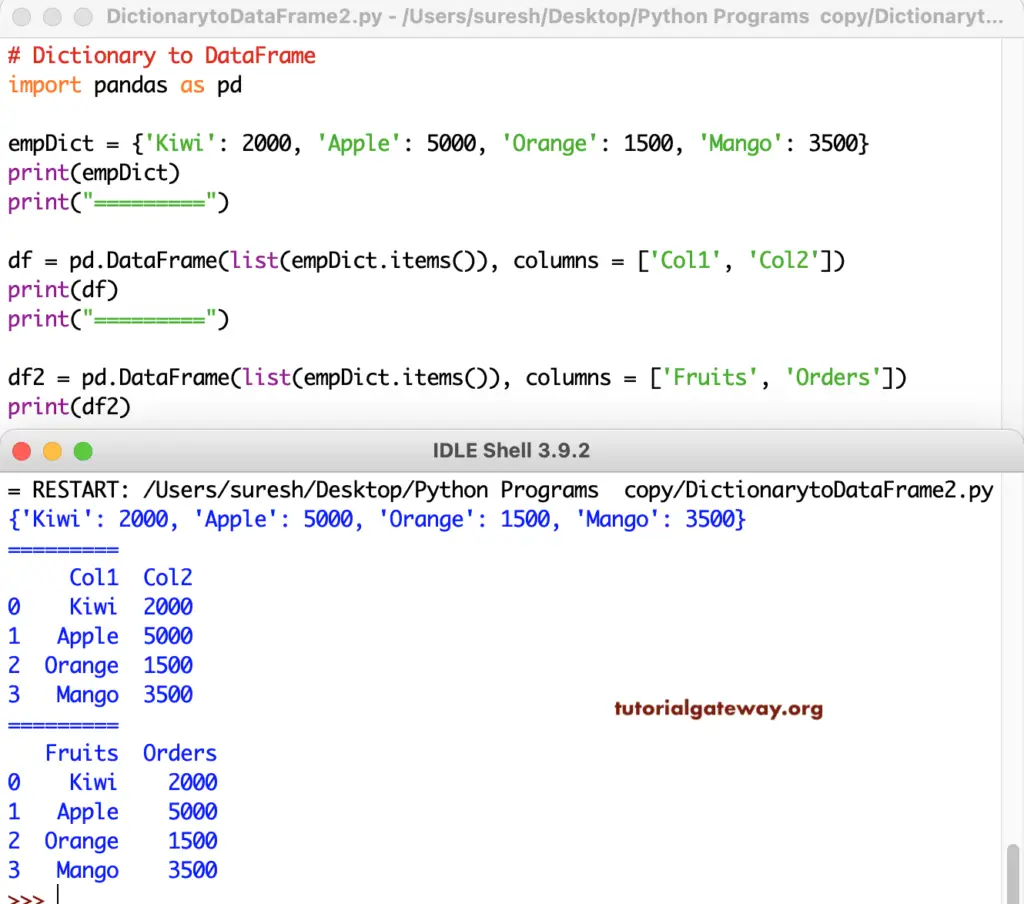
empDict = {'Kiwi': 2000, 'Apple': 5000, 'Orange': 1500, 'Mango': 3500}
print(empDict)
print("=========")
df = pd.DataFrame(list(empDict.items()), columns = ['Col1', 'Col2'])
print(df)
print("=========")
df2 = pd.DataFrame(list(empDict.items()), columns = ['Fruits', 'Orders'])
print(df2)
Convert Dictionary to Pandas DataFrame in Python
Although the above examples work great, you don’t need that much work to convert Dictionary to DataFrame. The from_dict() function converts the dictionaries, or you can straight away use that one within the DF function. The Coll part is that it automatically assigns the column names.
empDict = {'name': ['Jhon', 'Mike', 'Dave', 'Kane', 'Rose'],
'Age': [32, 37, 25, 29, 23]}
df1 = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(empDict)
print(df1)
print("== === == == == === == == == ")
df2 = pd.DataFrame(empDict)
print(df2)
name Age
0 Jhon 32
1 Mike 37
2 Dave 25
3 Kane 29
4 Rose 23
== === == == == === == == ==
name Age
0 Jhon 32
1 Mike 37
2 Dave 25
3 Kane 29
4 Rose 23The from_dict() function has an orient attribute, and its default value is columns to assign column names from Dictionary. If you change the orient to index, the Dict will pivot or transpose and pass to df.
empDict = {'name': ['Jhon', 'Mike', 'Dave', 'Kane', 'Rose'],
'Age': [32, 37, 25, 29, 23]}
df1 = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(empDict, orient = 'columns')
print(df1)
print("== == == == == ==")
df2 = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(empDict, orient = 'index')
print(df2)
print("== == == == == ==")
df3 = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(empDict, orient = 'index',
columns = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e'])
print(df3)
name Age
0 Jhon 32
1 Mike 37
2 Dave 25
3 Kane 29
4 Rose 23
== == == == == ==
0 1 2 3 4
name Jhon Mike Dave Kane Rose
Age 32 37 25 29 23
== == == == == ==
a b c d e
name Jhon Mike Dave Kane Rose
Age 32 37 25 29 23This Programming example shows multiple ways to convert the nested Dictionary to pandas DataFrame.
empDict = [{'name': 'Jhon', 'Age': 32, 'Job': 'Developer'},
{'name': 'Dave', 'Age': 29, 'Job': 'Designer'},
{'name': 'Rose', 'Age': 23, 'Job': 'HR'},
{'name': 'Mike', 'Age': 41, 'Job': 'Manager'},
{'name': 'Kane', 'Age': 37, 'Job': 'Admin'} ]
df1 = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(empDict)
print(df1)
print("== == == === == == ==")
df2 = pd.DataFrame(empDict)
print(df2)
name Age Job
0 Jhon 32 Developer
1 Dave 29 Designer
2 Rose 23 HR
3 Mike 41 Manager
4 Kane 37 Admin
== == == === == == ==
name Age Job
0 Jhon 32 Developer
1 Dave 29 Designer
2 Rose 23 HR
3 Mike 41 Manager
4 Kane 37 AdminWe can use the columns argument to remove or reorder the dictionary columns based on our requirements. First, we reorder the Age and Job columns. Next, remove the age column and add the Sx column. That’s why it returns the Sx column with NaN rows.
import pandas as pd
empDict = [{'name': 'Jhon', 'Age': 32, 'Job': 'Developer'},
{'name': 'Dave', 'Age': 29, 'Job': 'Designer'},
{'name': 'Rose', 'Age': 23, 'Job': 'HR'},
{'name': 'Mike', 'Age': 41, 'Job': 'Manager'},
{'name': 'Kane', 'Age': 37, 'Job': 'Admin'} ]
df1 = pd.DataFrame(empDict, columns = ['name', 'Job', 'Age'])
print(df1)
print("== == == === == == ==")
df2 = pd.DataFrame(empDict, columns = ['name', 'Job'])
print(df2)
print("== == == === == == ==")
df3 = pd.DataFrame(empDict, columns = ['name', 'Job', 'Age', 'Sx'])
print(df3)
name Job Age
0 Jhon Developer 32
1 Dave Designer 29
2 Rose HR 23
3 Mike Manager 41
4 Kane Admin 37
== == == === == == ==
name Job
0 Jhon Developer
1 Dave Designer
2 Rose HR
3 Mike Manager
4 Kane Admin
== == == === == == ==
name Job Age Sx
0 Jhon Developer 32 NaN
1 Dave Designer 29 NaN
2 Rose HR 23 NaN
3 Mike Manager 41 NaN
4 Kane Admin 37 NaNIt is a real-time scenario of the dictionaries that you might see. Here, we have shown multiple ways to convert these kinds of ones. I suggest you try one more nested.
empDict = {'Employee': {'Q1': 'Jhon', 'Q2': 'Dave', 'Q3': 'Mike', 'Q4': 'Rose'},
'2018':{'Q1': 1200, 'Q2': 1000, 'Q3': 2500, 'Q4': 600},
'2019':{'Q1': 2500, 'Q2': 3200, 'Q3': 1800, 'Q4': 4500},
'2020':{'Q1': 1700, 'Q2': 3200, 'Q3': 5000, 'Q4': 8000}
}
df1 = pd.DataFrame(empDict)
print(df1)
print("== == == === == == ==")
df2 = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(empDict)
print(df2)
Employee 2018 2019 2020
Q1 Jhon 1200 2500 1700
Q2 Dave 1000 3200 3200
Q3 Mike 2500 1800 5000
Q4 Rose 600 4500 8000
== == == === == == ==
Employee 2018 2019 2020
Q1 Jhon 1200 2500 1700
Q2 Dave 1000 3200 3200
Q3 Mike 2500 1800 5000
Q4 Rose 600 4500 8000It is another example.
empDict = {'Employee': {2018: 'Jhon', 2019: 'Dave', 2020: 'Mike'},
'Q1':{2018: 1200, 2019: 1000, 2020: 2500},
'Q2':{2018: 2500, 2019: 3200, 2020: 1800},
'Q3':{2018: 1700, 2019: 3200, 2020: 5000},
'Q4':{2018: 1600, 2019: 4500, 2020: 8000}
}
df1 = pd.DataFrame(empDict)
print(df1)
print("== == == === == == ==")
df2 = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(empDict)
print(df2)
Employee Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
2018 Jhon 1200 2500 1700 1600
2019 Dave 1000 3200 3200 4500
2020 Mike 2500 1800 5000 8000
== == == === == == ==
Employee Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4
2018 Jhon 1200 2500 1700 1600
2019 Dave 1000 3200 3200 4500
2020 Mike 2500 1800 5000 8000