In this section, we show how to connect Talend to Db or Database using a context group with a practical approach. Using the context group to connect Talend to DB or database is the best approach. Because, once you move your project production, you have to change these Talend context variables to connect with the production database.
Before we start connecting Talend to DB, let me show you the list of available context groups. Please refer to Create Context Group article to understand the context groups.
Connect Talend to DB using Context Group
Please drag and drop the Talend tDBConnection from the palette to Job design.
Within the tDBConnection Component tab, please select the Microsoft SQL Server as the Database type and click the Apply button.
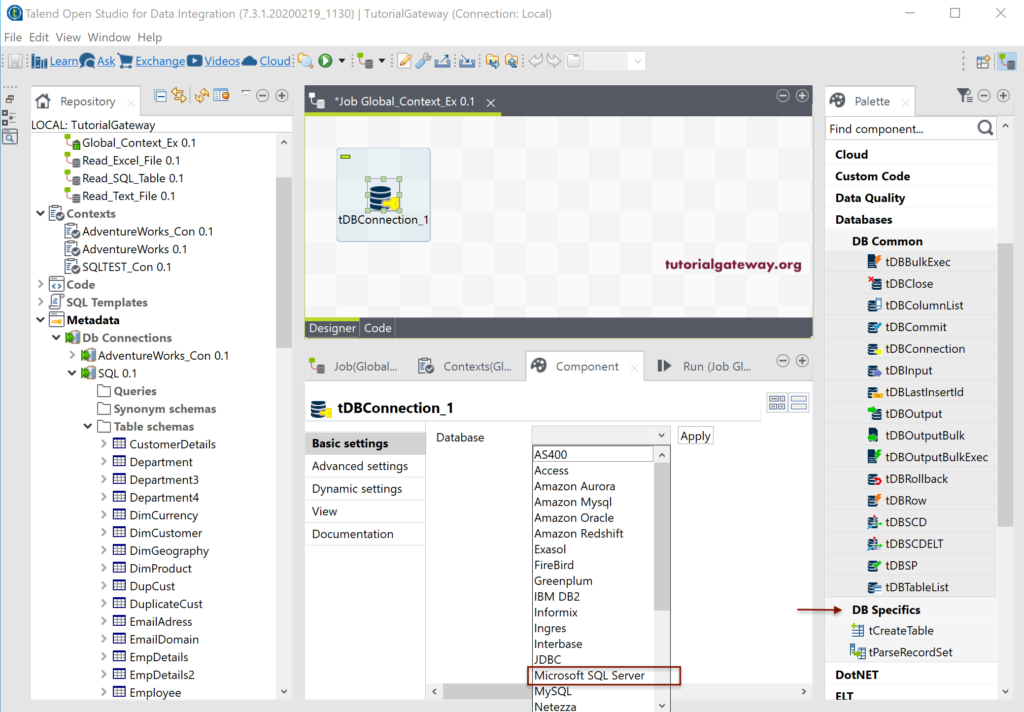
Next, drag and drop the SQLTEST_Con context group from the repository to the Contexts tab. From the below Talend screenshot, you can see all the values in that global context group.
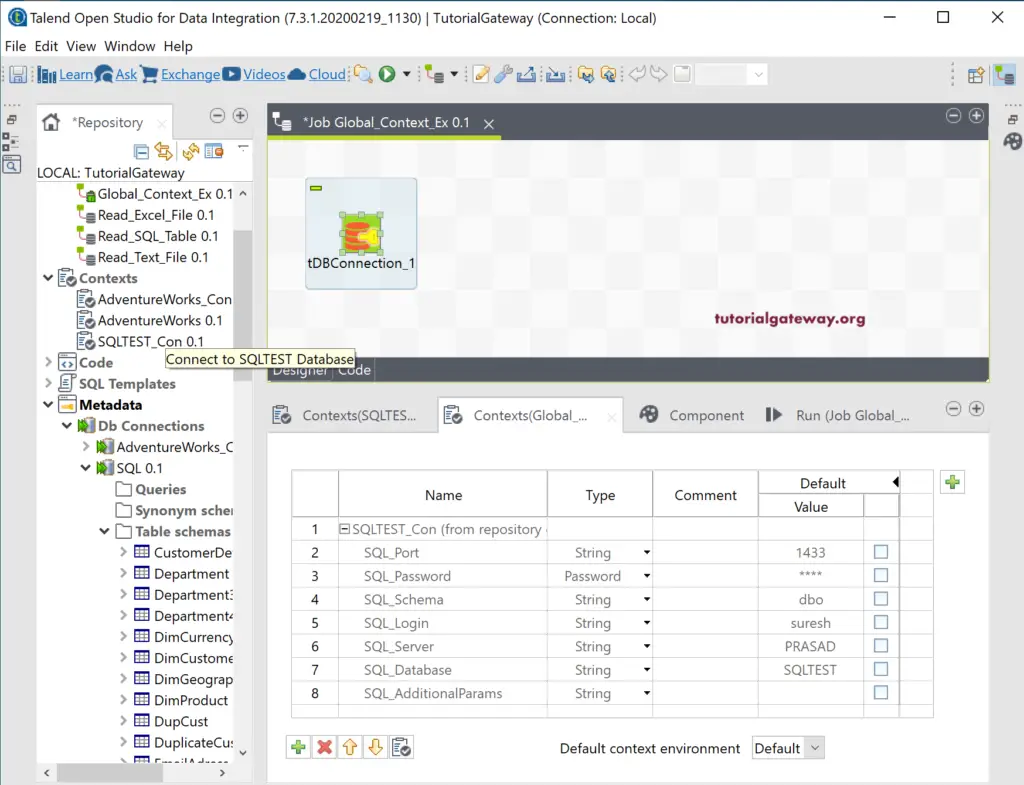
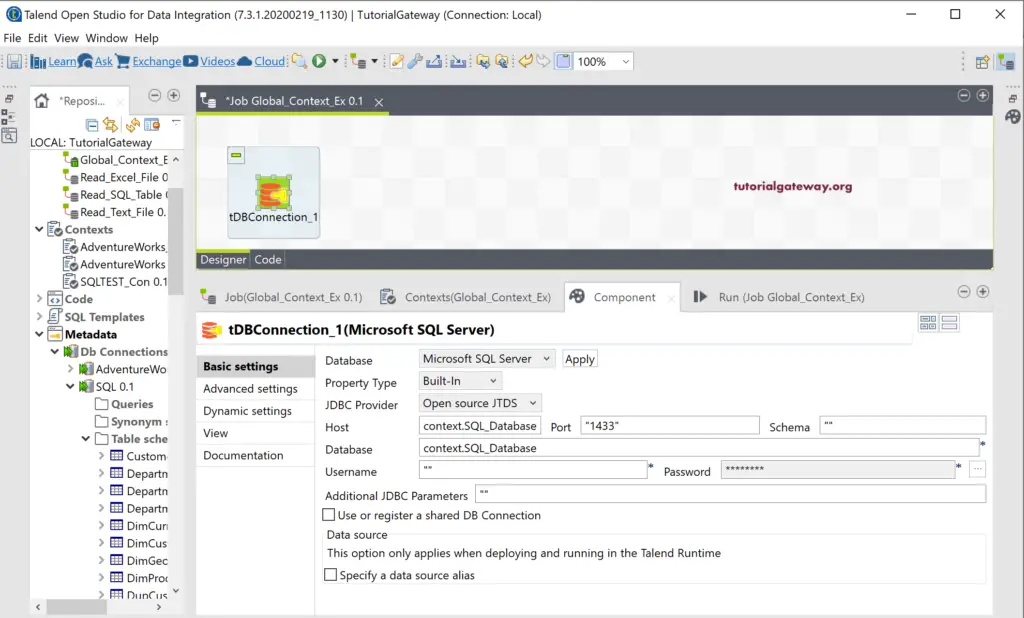
Please go to the Component tab to fill all the details to establish a connection with the SQL Database. Please fill the Host, Database, Username, Password, and Schema values with the context group variables. To access each context variable, you have use context.variable_name or type context. and ctrl+space. It will display all the viable context variables.
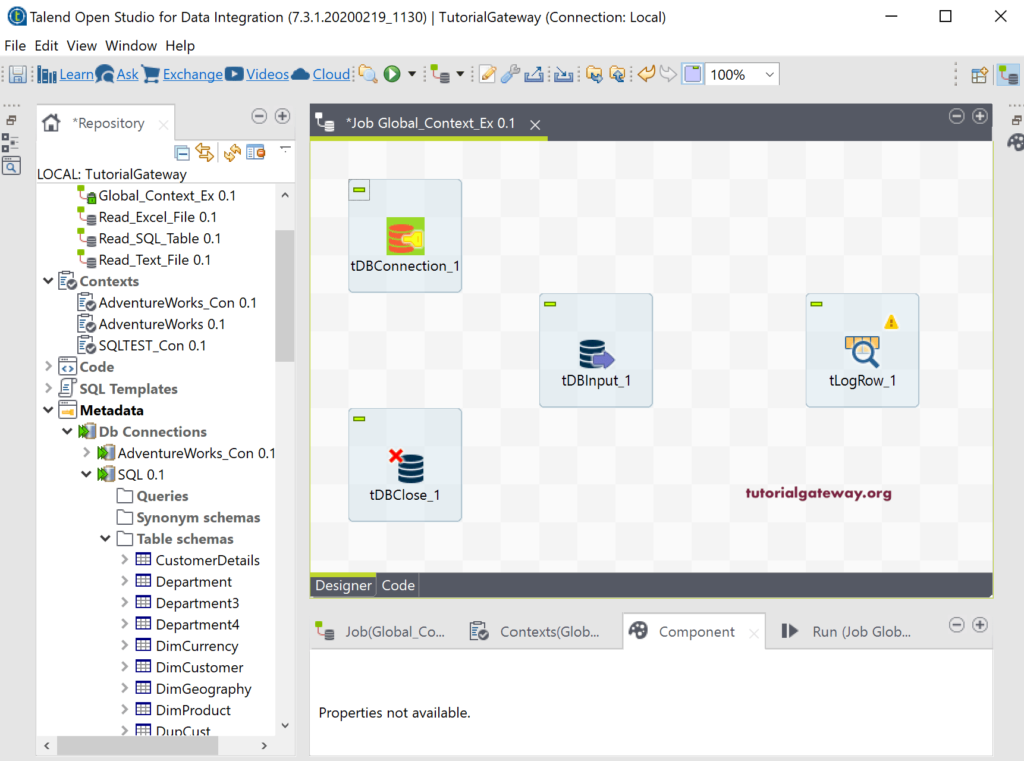
Next, drag and drop the tDBClose, tDBInput, and tLogRow from the palette to Job design.
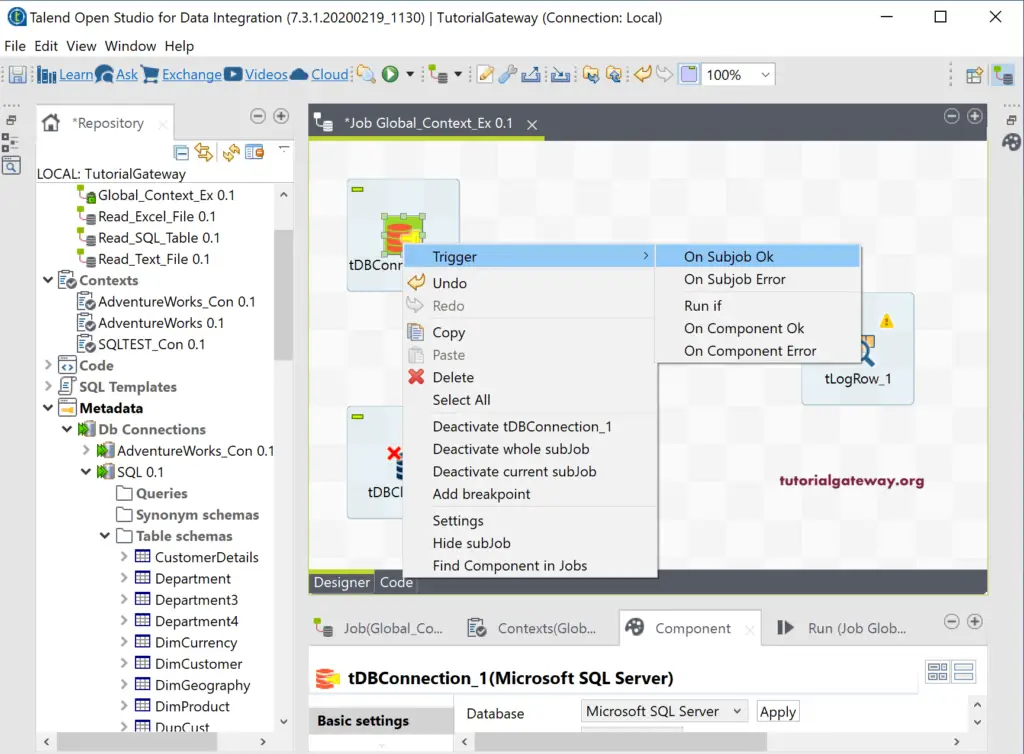
Right-click on the tDBConnections and select Trigger and choose On Subjob Ok and join it to tDBInput. It means that once the connection with SQL Server established, it will go to the next sub job.
Before we connect DBConnections and tDBInput, you have to specify the server that you are working with. I mean, we haven’t selected the DB specific tDBInput, so, first, we have to select the Database type.
You can see from the below screenshot, we have selected the Database as the Microsoft SQL Server. Next, check-marked the Use an existing connection option, and chose the tDBConnection_2 that we created in the tDBConnection field.
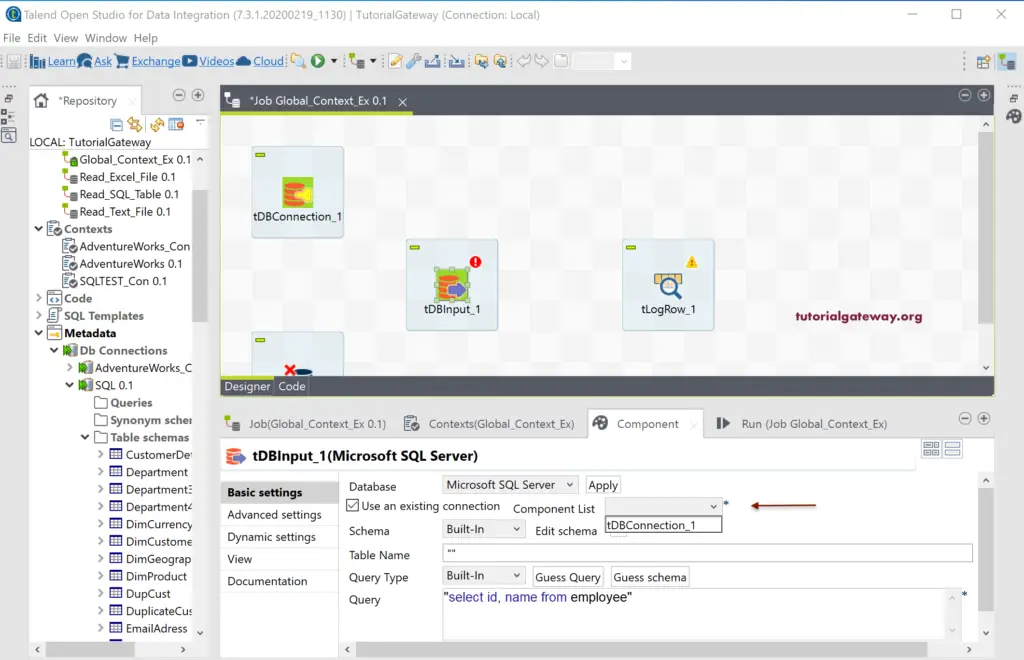
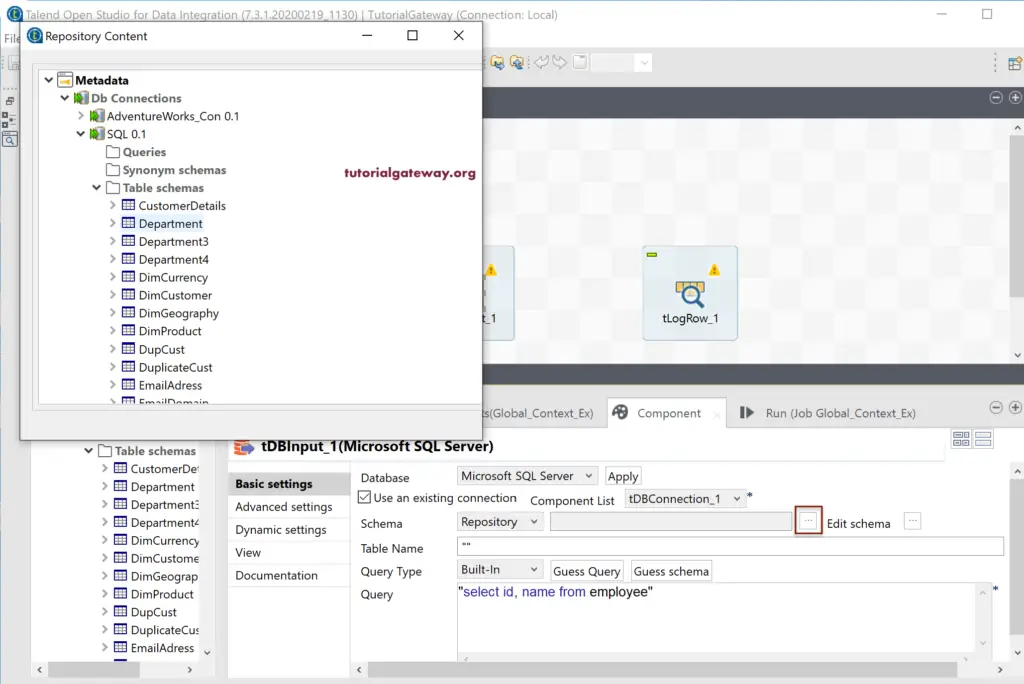
Next, change the Talend Schema from Built-in to Repository and click the Browse button to select the Schema or Table. Clicking on the browse button opens the following window, and we chose the Department table.
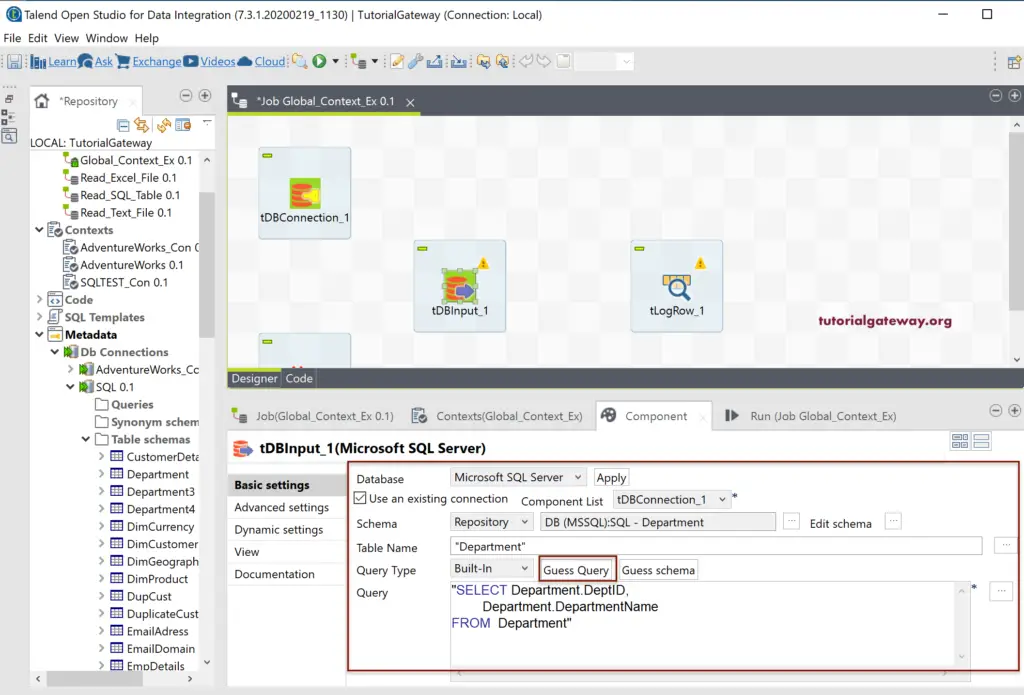
Mostly, it will generate the Query for the selected table. If not, please click the Guess Query button.
Next, connect the tDBInput main row with tLogRow with Table mode.
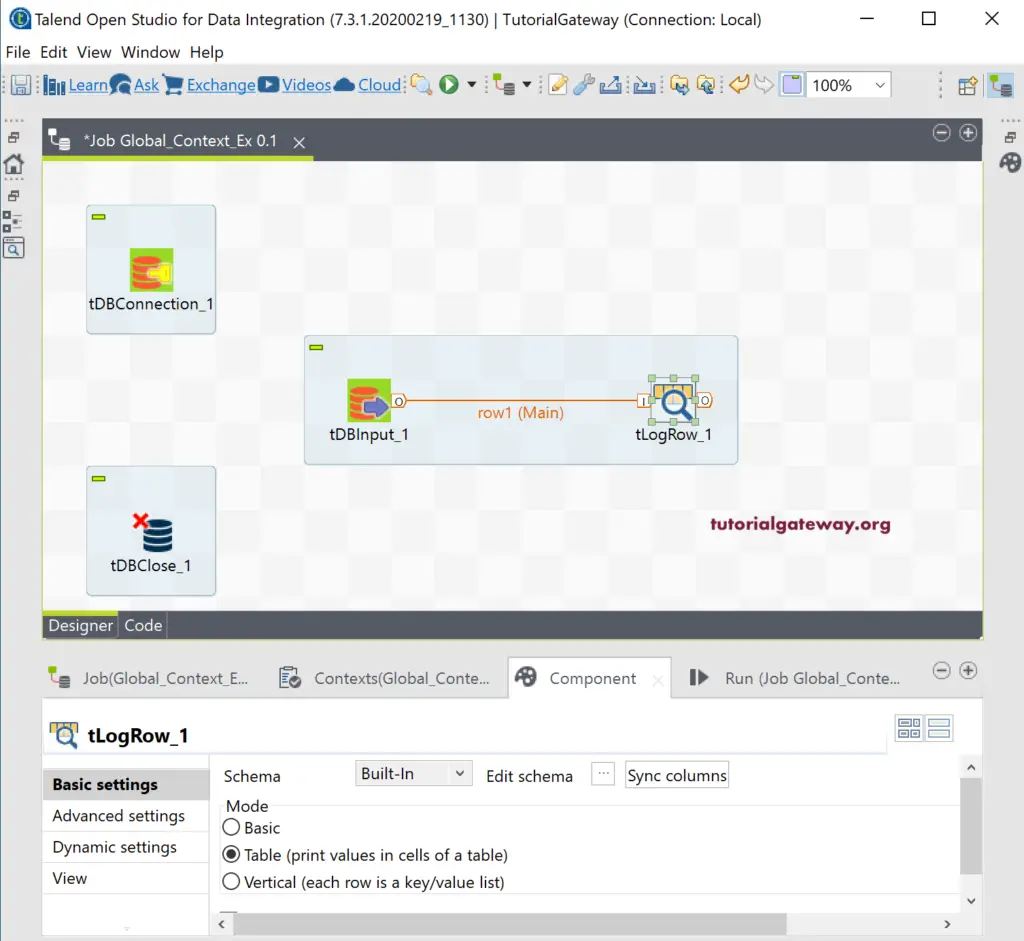
Please go to the tDBClose components tab, and select the Microsoft SQL Server as the Database, and choose the existing connection name from the Components list. Generally, we use the tDBCommit component, which has the same property along with a close connection option. The tDBCommit used to commit the change in the DB, and here, we are just reading the records or rows from a table. So, tDBClose will do the work, and it also helps us to introduce a new field.
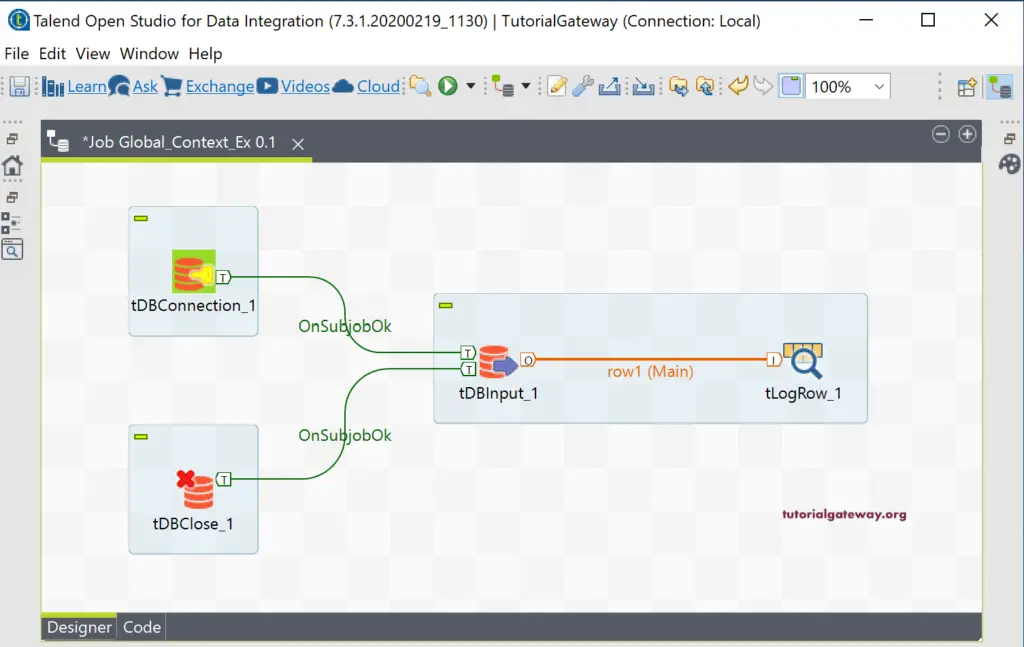
Right-click on the tDBConnections and select Trigger and choose On Subjob Ok and join it to tDBInput. Next, Right-click on the tDBInput and select Trigger and choose On Subjob Ok and join it to tDBClose or tDBCommit.
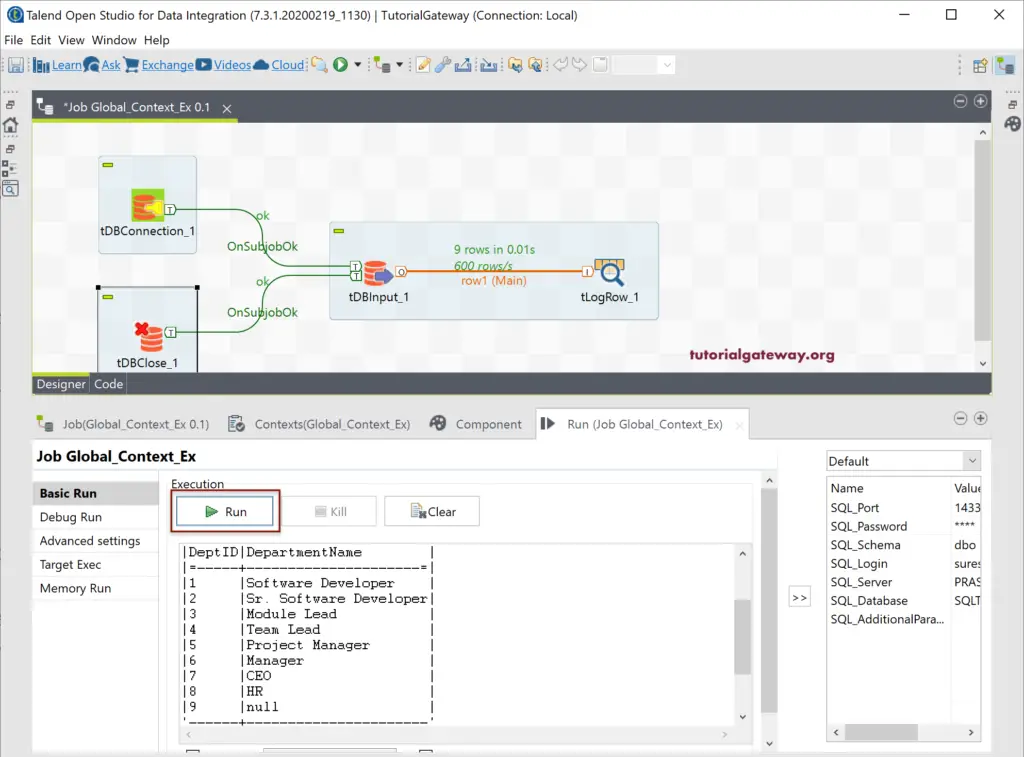
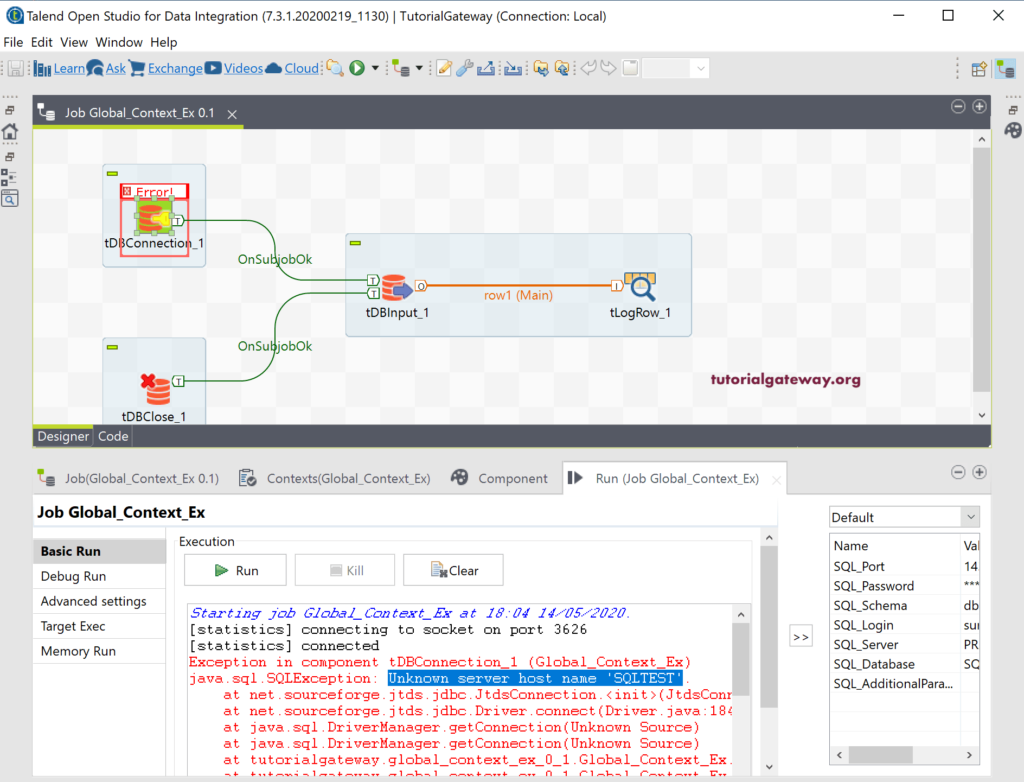
Let me run this connect Talend to DB or Database using context group Job and see. Ohh! We got an error saying Server hostname ‘SQLTEST’. Hostname means Server name, i.e., Prasad and SQLTEST is a Database name. I think I made a mistake while assigning the context variables to the tDBConnection components.
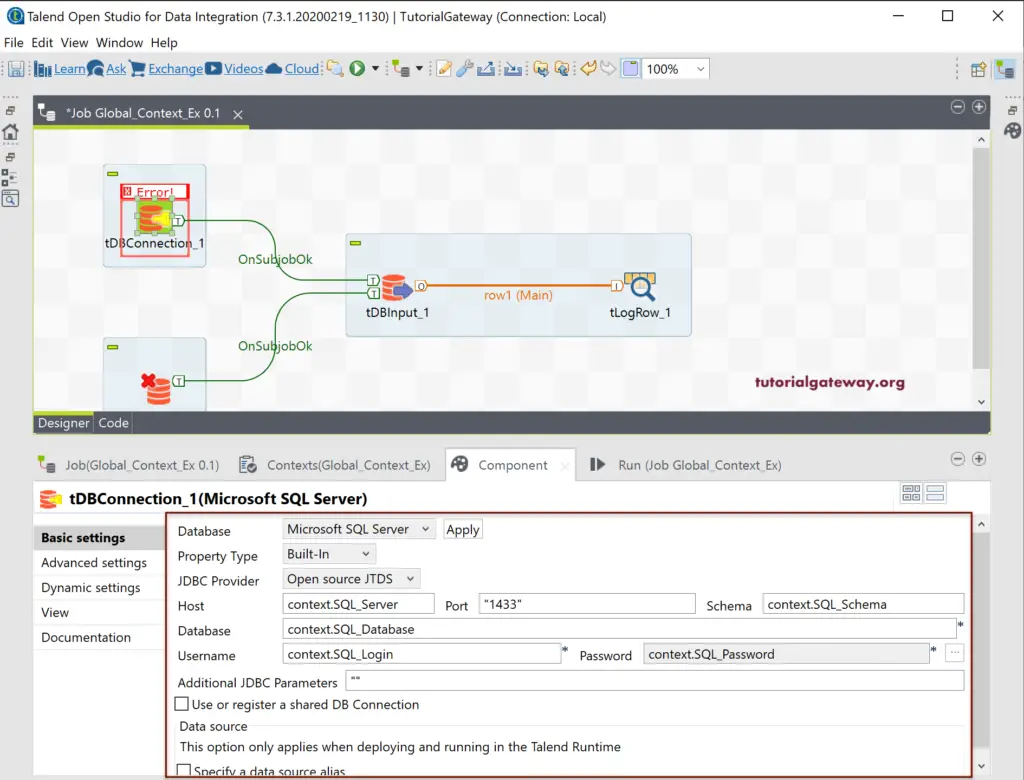
From the below screenshot, you can see that we fixed all the issues.
Now you can see the records from the Department table.